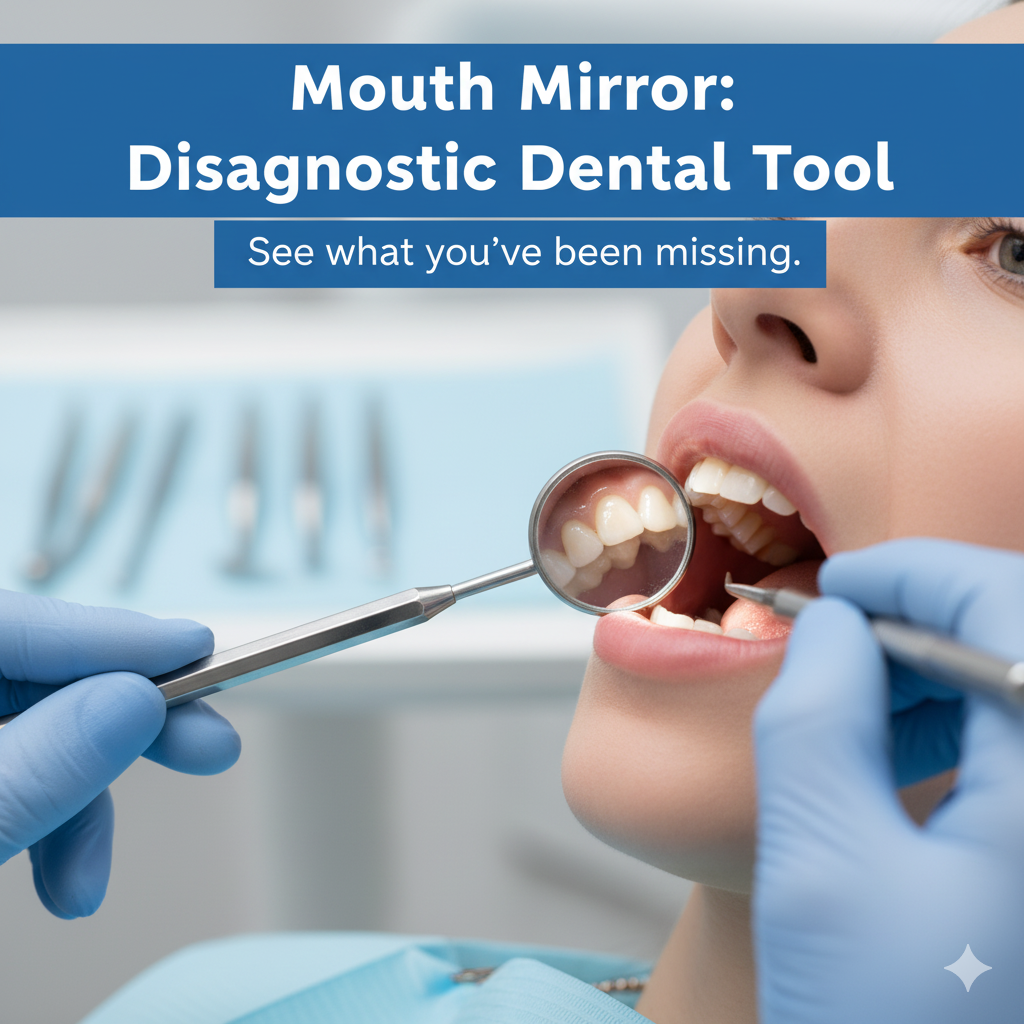
In the field of clinical prosthodontics, precision, visibility, and accuracy are the foundations of successful dental treatment. Among the numerous instruments used by dental professionals, the mouth mirror holds a place of great importance. Despite its simple design, this diagnostic tool plays a vital role in facilitating examination, diagnosis, and treatment planning. This is a small, round, concave or flat mirror attached to a slender metal handle, specifically designed to assist dentists in visualizing areas of the mouth that are otherwise difficult to see directly.
The mouth mirror not only enhances visibility inside the oral cavity but also aids in illumination, retraction, and indirect vision, making it one of the most indispensable instruments in a prosthodontic setup.
What Is a Mouth Mirror?
This is a diagnostic dental instrument that consists of two main components — a mirror head and a handle. The mirror head is usually circular and available in various diameters (commonly 18–24 mm), while the handle provides a firm and ergonomic grip for the clinician. The mirror surface may be plane (flat) or concave, depending on the level of magnification required.
In prosthodontics, the mouth mirror is essential for assessing the oral cavity before, during, and after dental procedures such as crown preparation, denture fabrication, or implant placement. It allows the dentist to observe hidden surfaces of teeth, evaluate soft tissues, and assess occlusion and alignment, all of which are critical in prosthodontic diagnosis and treatment planning.
Types of Mouth Mirrors
It comes in several variations based on its reflecting surface and construction. Understanding these types helps clinicians choose the right tool for specific procedures.
1. Plane (Flat) Mouth Mirror
A plane mouth mirror has a flat reflective surface that provides a true image without magnification. Although it may cause slight double images when used indirectly, it is ideal for general examination and simple diagnostic tasks.
2. Concave Mouth Mirror
The concave mirror produces a magnified image of the examined area, which enhances visibility of small structures, fine details, and surface irregularities. This type is particularly useful in prosthodontics for detecting marginal discrepancies in crowns, bridges, or dentures.
3. Front Surface Mirror
A front surface mouth mirror eliminates ghost images by placing the reflective coating on the outer surface of the glass. This ensures a sharp, clear, and distortion-free reflection. It is widely used in modern prosthodontic clinics for precision-based diagnostic work.
Functions and Uses of a Mouth Mirror in Prosthodontics
It serves multiple functions that make it indispensable in diagnostic and operative dentistry. Its primary uses include:
1. Indirect Vision
One of the most important uses of the mouth mirror is providing indirect vision for areas that are not directly visible, such as the posterior surfaces of teeth or the lingual surfaces of mandibular molars. This is essential during prosthodontic impressions, crown fittings, and occlusal evaluations.
2. Illumination
By reflecting light onto dark or shadowed areas of the mouth, the mouth mirror enhances illumination. This improves visualization of fine details, enabling the clinician to make more accurate diagnoses.
3. Retraction of Soft Tissues
It helps retract the tongue, lips, and cheeks, providing better access to the working area without causing patient discomfort. This is especially important during impression-taking, tooth preparation, and fitting prostheses.
4. Transillumination
When light is reflected through anterior teeth using the mirror, it helps reveal caries, cracks, or structural defects — an essential step in comprehensive diagnostic procedures. (Wikipedia)
Importance of Mouth Mirror in Clinical Prosthodontics
In clinical prosthodontics, the mouth mirror is more than a visual aid — it is a diagnostic necessity. Accurate examination of oral structures determines the success of prosthetic rehabilitation. The instrument allows the prosthodontist to:
- Detect tooth wear, fractures, and surface irregularities.
- Examine soft tissue health before denture placement.
- Assess alignment, occlusion, and spacing crucial for prosthesis design.
- Evaluate fit and finish of crowns, bridges, and dentures.
Without the clarity and accessibility provided by the mouth mirror, diagnosing complex cases or evaluating prosthodontic outcomes would be nearly impossible.
Components and Design of a Mouth Mirror
A standard mouth mirror consists of:
- Handle: Usually made of stainless steel, ergonomically designed for comfort and control.
- Stem or Shank: Connects the handle to the mirror head, angled to allow optimal access.
- Mirror Head: Available in various sizes and shapes; detachable designs enable easy sterilization and replacement.
Modern mouth mirrors may also feature anti-fog coatings, fiber-optic illumination, or disposable mirror heads, enhancing efficiency and infection control.
Maintenance and Sterilization
Since the mouth mirror comes into direct contact with the patient’s oral cavity, proper cleaning and sterilization are critical. After each use, the mirror should be:
- Rinsed with water to remove debris.
- Ultrasonically cleaned using an enzymatic solution.
- Sterilized using an autoclave to ensure elimination of pathogens.
- Stored in sterile pouches until the next use.
Neglecting these steps can lead to cross-contamination, compromising patient safety and clinical hygiene.
Conclusion
It may appear to be a simple tool, but its importance in clinical prosthodontics cannot be overstated. As one of the most vital diagnostic instruments, it allows dentists to examine, diagnose, and treat with precision. From providing indirect vision and illumination to retracting soft tissues, It supports nearly every aspect of dental examination and prosthodontic procedures.
Maintaining high-quality mouth mirrors, ensuring proper sterilization, and choosing the right type for specific procedures are essential practices for every dental professional committed to excellence in patient care.