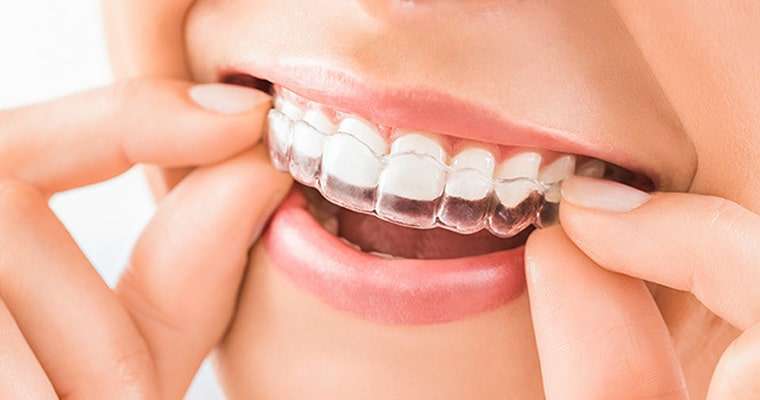
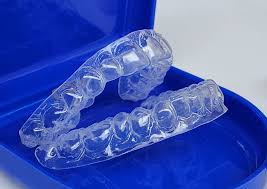
Night guards are custom-made, removable appliances typically made from rigid or semi-rigid thermoplastics (e.g., ethylene-vinyl acetate [EVA], acrylic, or dual-laminate materials) worn over the teeth to protect against bruxism, clenching, or TMJ issues. Unlike restorative solutions (zirconia: 700–1,200 MPa, E-max: 360–500 MPa, dentures) or bleaching trays, night guards are non-restorative, focusing on protection and symptom relief. They are designed for durability and occlusal stability, leveraging CAD/CAM and occasionally DSD for precision and patient comfort.
Advantages of Night Guard Design
- Tooth Protection: Prevents wear from bruxism, complementing restorations like E-max or zirconia.
- TMJ Relief: Reduces muscle/joint stress in TMJ disorders, unlike non-functional bleaching trays.
- Non-Invasive: No tooth prep, like bleaching trays or dentures, unlike crowns (0.4–1.5 mm reduction).
- Digital Workflow: CAD/CAM ensures precise fit, similar to temporary crowns or E-max workflows.
- Comfort: Soft or dual-laminate materials are more comfortable than rigid acrylic dentures for nightly wear.
CAD Design
- Software: Import scans into CAD software (e.g., exocad, 3Shape Splint Studio).
- Night Guard Design:
- Thickness: Design a 1.5–3.0 mm thick guard (1.5–2 mm for soft EVA, 2–3 mm for hard acrylic or dual-laminate) to balance durability and comfort. Thicker than bleaching trays (0.5–1.0 mm) but thinner than acrylic denture bases (2–3 mm).
- Coverage: Cover all teeth in one arch (usually maxillary; mandibular for specific TMJ cases). Extend 1–2 mm beyond gingival margins for retention, with smooth, non-scalloped edges (unlike bleaching trays).
- Occlusal Surface: Design a flat occlusal plane for even contact with opposing teeth, minimizing stress. For TMJ relief, incorporate anterior guidance (canine rise) or slight disclusion (1–2 mm).
- Retention: Ensure a snug fit to teeth without undercuts for easy insertion/removal, similar to bleaching trays but more robust.
- Parameters:
- Material: Specify EVA (soft, 0.080–0.120 inches), acrylic (hard, e.g., Splint Acrylic), or dual-laminate (soft inner, hard outer) based on bruxism severity.
- Occlusion: Adjust for minimal interference (0.5–1.0 mm disclusion for TMJ guards) using virtual articulators.
- Comfort: Smooth all edges to prevent tissue trauma.
- Esthetics: Use clear or translucent materials (e.g., Essix ACE) for anterior visibility, guided by DSD if esthetics are a concern.